Short Definition Of Buffer Solution
In other words a buffer is an aqueous solution of either a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components.
 Hydrogen Bonding Definition Examples And Types Digital Kemistry Hydrogen Bond Bond Molecules
Hydrogen Bonding Definition Examples And Types Digital Kemistry Hydrogen Bond Bond Molecules
A buffer is an aqueous solution that consists of a mixture of a weak acid and its salt acid buffer or a weak base with its salt basic buffer.

Short definition of buffer solution. Buffer bŭf ər Chemistry A substance that prevents change in the acidity of a solution when an acid or base is added to the solution or when the solution is diluted. A biological buffer is an organic substance that has a neutralizing effect on hydrogen ions. A lot of biological and chemical reactions need a constant pH for the reaction to proceed.
To lessen the shock of. Definition A buffer solution is one which resists changes in pH when small quantities of an acid or an alkali are added to it. This is important for processes andor reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges.
Any substance or mixture of compounds that added to a solution is capable of neutralizing both acids and bases without appreciably changing the original acidity or alkalinity of the solution. A solution containing such a substance. Buffer in chemistry solution usually containing an acid and a base or a salt that tends to maintain a constant hydrogen ion concentration.
Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications. A buffer solution more precisely pH buffer or hydrogen ion buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa. A buffer solution is chemical solution which resists change to its pH or acidity.
A buffer solution is a solution containing weak acids and their conjugate bases or weak bases and conjugated acids that are resistant to pH changes. Phosphate KH2PO4 solution were prepared and the pH was measured to be 987 and 423 respectively th e solution were made usin g 1N Hcl and 5N NaoH respectively and the pH was found to be 65. Most buffers consist of a weak acid and a weak base.
A buffer system has the property of resisting pH changes despite additions of acid or base. A buffer solution more precisely pH buffer or hydrogen ion buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa Use of the term in Sentences. In this way a biological buffer helps maintain the body at the correct pH so that biochemical processes continue to run optimally.
A buffer may also be called a pH buffer hydrogen ion buffer or buffer solution. Buffers are solutions that resist a change in pH on dilution or on addition of small amounts of acids or alkali. In other words a buffer is an aqueous solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
In other words a buffer is a solution that is able to maintain the pH condition of a solution. A solution that usually contains on the one hand either a weak acid as carbonic acid together with one of the salts of this acid or with at least one acid salt of a weak acid or on the other hand a weak base as ammonia together with one of the salts of the base and that by its resistance to changes in hydrogen-ion concentration on the addition of acid or base is useful in many chemical biological and technical processes. Buffers are used to make solutions of known pH especially for instrument calibration purposes.
It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable. To prepare aspirin with an antacid. To treat something such as an acid solution with a buffer also.
An example of a common buffer is a solution of acetic acid CH 3 COOH and sodium acetate. A buffer is a solution containing either a weak acid and its salt or a weak base and its salt which is resistant to changes in pH. In chemistry buffer solution and examplesIt is a solution containing either a weak acid and its salt or a weak base and its salt which resists changes in pH.
Meaning of Buffer System. Also called buffer solution. Buffers are extremely useful in these systems to maintain the pH at a constant value.
Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. This does not mean that the pH of buffers does not change. Definition of buffer Entry 3 of 4 transitive verb.
It is a solution in water of a mixture of a weak acid or base and its salt. To collect data in a buffer. The pH of the solution changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it.
Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it and is thus used to prevent a solution s pH change. Chemists use buffer solutions to keep the pH level at nearly a constant value among different types of chemical applications. Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons.
A buffer is a mixture of an acid that does not ionize completely in water and its corresponding base-for example carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 and sodium bicarbonate NaHCO 3.
 Caramelization In Cooking Caramelization Reactions Chemistry Biological Chemistry Caramel Flavoring
Caramelization In Cooking Caramelization Reactions Chemistry Biological Chemistry Caramel Flavoring
Buffer Solution Solution Of Reserve Acidity Alkalinity
 Coordinate Covalent Bond Definition Examples Formation And Properties Covalent Bonding Coordinates Cool Websites
Coordinate Covalent Bond Definition Examples Formation And Properties Covalent Bonding Coordinates Cool Websites
 Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs Sodium Chloride Electrolysis Half Reactions Oxid Chemistry Redox Reactions Informative
Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs Sodium Chloride Electrolysis Half Reactions Oxid Chemistry Redox Reactions Informative
 Why Bond Length Decreases With Bond Multiplicity Bond Length Electron Configuration Chemistry Lessons
Why Bond Length Decreases With Bond Multiplicity Bond Length Electron Configuration Chemistry Lessons
 Chemistry Super Animated Videos Examples Of Plasma Blog Posts Chemistry Blog
Chemistry Super Animated Videos Examples Of Plasma Blog Posts Chemistry Blog
 Law Of Mass Action 11th Chemistry Chemistry Chemical Reactions
Law Of Mass Action 11th Chemistry Chemistry Chemical Reactions
 Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Solutions Electron Configuration
Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Solutions Electron Configuration
 What Is Evaporation Evaporation Molecules Chemistry
What Is Evaporation Evaporation Molecules Chemistry
 Fsc Chemistry Video Lecturers Digital Kemistry Youtube Functional Groups Organic Chemistry Functional Group Chemistry Class 12
Fsc Chemistry Video Lecturers Digital Kemistry Youtube Functional Groups Organic Chemistry Functional Group Chemistry Class 12
 Vapour Pressure And Boiling Point Chemistry Class Boiling Point Vapor
Vapour Pressure And Boiling Point Chemistry Class Boiling Point Vapor
 Bicarbonate Buffer System Example Of Multiple Equilibria Teaching Chemistry Medical School Studying Biochemistry
Bicarbonate Buffer System Example Of Multiple Equilibria Teaching Chemistry Medical School Studying Biochemistry
 Buffers Definition Overview Expii
Buffers Definition Overview Expii
 Boiling Point Class 11 12 Boiling Point And External Pressure Boiling Point Chemistry States Of Matter
Boiling Point Class 11 12 Boiling Point And External Pressure Boiling Point Chemistry States Of Matter
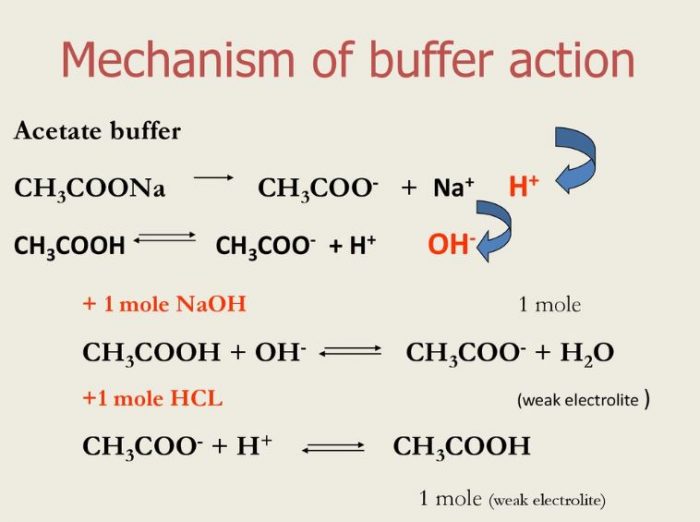 Buffer Solution And Buffer Action Chemistry Class 11 Ionic Equilibrium
Buffer Solution And Buffer Action Chemistry Class 11 Ionic Equilibrium
 Ph Chart For Acids And Bases Ph Chart Study Chemistry Electron Configuration
Ph Chart For Acids And Bases Ph Chart Study Chemistry Electron Configuration


